Artificial Intelligence and the Sustainable Development Goals
December 5, 2022
BUILDING AND DEVELOPING SMART CITY ATTACHES THE COMPREHENSION OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE WORLD SOCIETY (AIWS) UNDER THE IMPACTS OF THE FOURTH INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION (4.0)
Hanoi, January 27, 2021
Brief: The world is entering the fourth industrial revolution (4.0) with an expectation that humanity will gain new achievements, bringing people life with high satisfaction. However, this revolution also poses challenges from non-traditional security threats in four major groups of problems: environmental degradation, climate change, epidemics and international terrorism to every country, especially developing ones, which will face multiple challenges in terms of socio-economy, science – technology and ecological environment.
Towards the founding anniversary of 100 years of the United Nations (2045), in the UN Roundtable 2045, Ramu Damodaran, Chief of the United Nations Academic Impact initiative, Editor-in-Chief of the United Nations Chronicle and Vint Cerf, Father of the Internet discussed new model aimed at: “the human-centric economics, the internet ecosystem and new artificial intelligence for work and life “. The concept of AIWS City appears in the model of Smart city.
Keywords: Fourth Industrial Revolution (4.0), AIWS city, non-traditional security…
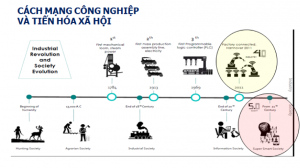
The “leverage” point is: AI (artificial intelligence); 3D printing technology, biotechnology, new materials industry, automation technology, robotics, internet of things (IoT) and internet of services (IoS). Industry 4.0 features the Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), first launched by Dr. Jame Truchat, CEO of National Instrument in 2006, in which the intelligent devices work together over a wireless network or through the “cloud”. The term “Industrie 4.0”, which began with the project in the German government’s CNC strategy, was first used in 2011 at the Hannover Fair; its definition and comprehension were officially identified at the 46th World Economic Forum (WEF) on January 20, 2016.
The scale of development is unprecedented in history, the growth rate is exponentially, exerting great impacts on the economy and ecological environment. The spread speed of technology in use reaches 50 million people (while telephone took 75 years, radio took 38 years, TV took 13 years, internet took 4 years, Facebook took 3.5 years to reach the same scale). In term of economy, this scale has impacts on consumption, production, productivity and price. The maps of the world economy and corporate strength are also being redrawn. For example, 3D printing technology worth $ 3.1 billion/year has increased by 35% compared to 2012; in the next 6 years, it will increase by an average of 32% to 21 billion USD by 2020.
Emerging occupations reflect a greater demand for jobs in the green economy; a leading role in data economy and AI; new roles in engineering, cloud computing and product development.
Developing jobs highlight the continuing importance of human interactions in the new economy through roles in the care economy; marketing, sales and content production.
By 2025, analytical, creative and flexible thinking will be one of the most sought-after skills. Recruiters consider critical thinking, analyzing and problem solving more and more important in the coming years. New highlights to this year are self-management skills, such as proactive learning, resilience, stress tolerance, and flexibility.
Impacts on the business: there are four main impacts on: (i) customer expectations, (ii) improving the quality of products and services, (iii) cooperative innovation and (iv) forms of production and creation. Increased pressure on immigration flows: The most competitive businesses will focus on improving the skills of their workers. Remote Working: About 84% of employers are rapidly digitizing work processes, dramatically expanding the form of teleworking. There is a chance that 44% of the workforce will move to remote working. However, 78% of entrepreneurs think there will be some negative impacts on workers’ productivity, and many firms are taking steps to help their employees adapt to work from home.
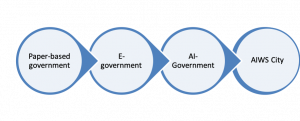
Impacts on government: the emergence of an AI-Government model. Towards the founding anniversary of 100 years of the United Nations (2045), in the UN Roundtable 2045, Ramu Damodaran, Chief of the United Nations Academic Impact initiative, Editor-in-Chief of the United Nations Chronicle and Vint Cerf, Father of the Internet discussed new model aimed at: “the human-centric economics, the internet ecosystem and new artificial intelligence for work and life”. The concept of AIWS City in the model of Smart city.
Government agencies’ ability to adapt to new technology will determine their managerial capacity. The government and its regulators will need to work closely with businesses, associations and citizens.
Impacts on people (human existence): biologically, socially, and mentally; creating new requirements.
Impacts on press and media: Automatic news writing technology: The software to automatically write financial news has been put into use by AP news agency since 2014 with the speed of up to 2,000 pieces of news/second and continuing to be expanded to other fields; AI creates media content by itself.
Impacts on security and defense: On November 1, 2002, the phrase “Non-Traditional Security” officially appeared in the ” ASEAN-China Joint Statement on cooperation in non-traditional security”. In view of the United Nations, there are 10 threats of non-traditional security (terrorism, drugs, piracy, money laundering, hackers, environmental disasters, epidemics, human trafficking, illegal and extreme migration and ethnicity, religion).
Taking advantage of internet connection to commit crimes; challenges in cyber and space (virtual) governance: Drones, Drones (unmanned objects). There were spikes in virtual space, virtual multi-level business, bubble of investment in virtual currencies, bitcoin has been causing crisis that spread to the global financial market without effective control measures.
In the 1st, 2nd and 3rd Industrial Revolutions in the past,different models of cities appeared: (1) Green city; (2) Eco city; (3) Garden city; (4) Ecological as Economic City (ECO2); (5) Sustainable development city (based on 3 pillars of economy, society, ecological environment); (6) Liverable City; (7) Recilient City.
Especially, in the fourth industrial revolution (4.0), characterized by system control, AI (Artificial Intelligence), IOT (Internet of Things), digital technology and robotics, connecting real world systems and virtual world, other models of cities appeared: (8) Cyber city, digital city, virtual city, knowledge city; (9) Smart city; (10) Smart city in association with Artificial Intelligence World Society (AIWS).
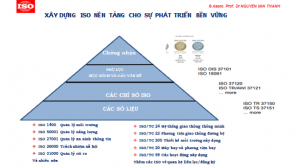
Cities meet ISO 37120: 2018 international standards (Sustainable cities and communities – Indicators for city services and quality of life. Sustainable development city and ISO 37122: 2019 (upgraded from ISO 37120: 2014) and ISO 37122:2019 cities (Sustainable cities and communities – Indicators for smart cities). ‘Smart city’ – the foundation that promotes an entrepreneurial society
According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the European Economic Commission of the United Nations (UNECE):
“A smart sustainable city is an innovative city that uses
information and communication technologies (ICTs) and other means to improve equality of life, efficiency of urban operation and services, and competitiveness, while ensuring that it meets the needs of present and future generations with respect to economic, social, environmental as well as cultural aspects”.
According to Bruno Peters , Ibi Group Smart City Taskforce Lead – October 2017:
A Smart City is a city or region that can increase its competitiveness and quality of life, efficiently use resources, and support economic sustainability by using technology and creativity to raise the IQ of the built environment.
Another approach: Smart city is a city that uses innovation to address the needs and desires of the community, puts the citizens first and ultimately breaks down the barriers between agencies and departments, and between people and government.
According to the Siment Center capacity research agency of cities: “Smart city is a city capable of connecting digital technology, providing efficient, utility services, optimizing infrastructure through the use of a large database of goals for integration, analysis and help providing better services, reduce financial pressure to create products: (1) Share benefits among elements; (2) Investment in infrastructure; (3) Connecting using resources between complex components; (4) The system is synchronized in the action plan; (6) Save time, efficient use of resources”
To fully understand smart city, in mind we need to perceive the city as an ecosystem, so we can generalize through the following concept:
“A Smart City is a city that uses cybernetic tools for connecting real world systems and the virtual world systems, the key is systems thinking and the means is using information and communications technologies. It aims to build characteristic, liveable, resilient and competitive cities. The measurement is the satisfaction of citizens and entails indicators of Security, Social welfare, Safety in the economy, society and environment…”
The role of information technology and communication in data collection, storage, transmission, calculation … with fast and cheap cost. Personal mobile device (smartphone, wearable); Cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT); Big data processing and social media. Devices that: (1) Sensor everywhere; (2) Stay connected anywhere; (3) – Data everywhere; (4) Service everywhere.

The orientation of building smart cities that meet ISO standards governing world cities, Smart city is a city that is speeding up providing sustainable results in terms of society, economy and environment and respond to challenges such as climate change, rapid population growth and political and economic uncertainty by fundamentally improving ways of participation in society, adopting collaborative leadership methods, comply with city rules and systems and use modern information and technology to provide better services and quality of life for people in the city (residents, businesses, visitors ) in the future and in the near future, not to adversely affect others or degrade the natural environment
City Governance Index: Designed to assist cities in directing and evaluating the performance management of city services as well as quality of life. Indicators will be reported on an annual basis. Depending on the goal of intelligence, cities will select the appropriate set of indicators from the ISO 37122: 2019 indicator set to the content and governance purposes according to ISO 37101 in terms of: Attraction ( ISO 37101); Social cohesion (ISO 37101); Happiness Level (ISO 37101); Responsible resource use (ISO 37101); Resilience (ISO 37101); Conserve and improve the environment (ISO 37101)
Ensuring security, safety and safety objectives adapt to Vietnamese conditions.
Smart city with groups of indicators ensure the following criteria: security, safety and safety:
Security Indicator:
1) Security for residents
2) Population security
3) Security for business
4) Monetary and financial security
5) Food security
6) Border and sea security
7) Connection security
8) Network security
9) Religious security
10) Rural security
11) Security of the databases
Social Security Indicator:
1) Economic sustainable development
2) Economic self-recovery, competitive ability
3) High quality of life
4) Care for vulnerable groups
5) Employment
6) Medical care
7) Elderly care
8) Education and training
9) Culture and spirit
10) Urban living space
11) Ease of access to urban and welfare services
12) Housing security
13) Transportation and public transport
14) Pensions and benefits
Safety Indicator:
1) Safety in crime reduction
2) Disease safety
3) Food safety
4) Traffic safety
5) Safe air environment
6) Water safety
7) Property safety
8) Personal information security
9) Safety in production and business
10) Fire and explosion safety
11) Safety of natural disasters and natural catastrophies
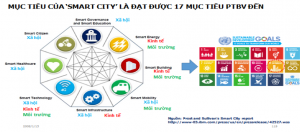
SWOT ANALYSIS (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) when building a smart city connected AIWS City (AI WORLD SOCIETY)
Trends in AI development today and in upcoming years
(1) – Chatbot virtual assistant – AI software helps to interact / talk automatically with each customer 24 hours / 7 days (64% of users choose to text rather than call or email). The interactive virtual assistant helps businesses save $ 8 billion by 2022. 25% of companies will use the customer service virtual assistant by 2020.
(2) – AI training time is reduced, automated machine learning can take in deeper knowledge
(3) – Speed up driverless cars (by 2030, driverless cars will reach 40%)
(4) – Automated machine learning (AutoML) and AI put into mass production (data science becomes the hottest profession), the application of AI tools is the most important trend in the following years.
(5) – AI can self-program applications, Combination of widespread artificial neural networks; Development of specialized AI systems
(6) – AI drives the transition to the digital economy; There might be a shortage of human resources with AI skills.
(7) – AI face recognition. AI chips enhance artificial intelligence. AI can recognize contexts and abstract concepts. AI can learn awareness, emotion
(8) – AI ethics: AI’s accountability and transparency In the near future, AI will: (i) -Design medical treatment regimens for patients; ii- Automatically search and select resumes of job-seeking candidates and make decisions on recruiting personnel for job positions. iii Automatically drive a car; iv – AI will participate in many other activities.
The problem arises: who will be responsible for accidents caused by AI designs, decisions, and AI devices? The problem of using non-transparent data sources, infringing on privacy, selling personal data of users without permission?
SWOT ANALYSIS (STRENGTHS, WEAKNESS, OPPORTUNITIES, CHALLENGES) OF AI
1) Provides a Better Quality of Life; (2) Fast processing speed, decision making; (3) Fast machine learning; (4) Large-scale development, (5) Brings about clear efficiency; (6) High precision; (7) Replaces people in managing many fields, reducing the need to use human resources; (8) Improves labor productivity
(1) Complex, requiring highly skilled human resources; (2) Still machine, unconscious for humans; (3) Bias or inaccuracy (AI learns from patterns in data, and may use false data thus making false, unrepresentative assumptions); (4) AI might possibily be superior to human intelligence; (5) Social responsibility; (6) The government is often slow to accept AI; (7) Requires the application of systematic thinking; (8) Requires large capital investment; (9) Need a large enough database for machine learning; (10) Requires information infrastructure, sensor system, broadband connection infrastructure; (11) Emotional machine learning problem?
(1) The global race on AI development starts in 2017; (2) The potential for a very wide range of applications; (3) Industry 4.0 very fast develops; (4) Great demands in all fields: media, defense, security, economics, social management, science, health, environmental protection, energy, finance, commerce, monitoring infrastructure management, forecasting, intelligent self-driving cars for people with disabilities … (5) Reduces stress for employees because AI can perform tedious and repetitive tasks on behalf of people; (6) The combination of AI and new forms of technology; (7) The AI market grows very fast; (8) Develop artificial intelligence government
(1) Job loss; (2) Awareness of AI is still limited; (3) There is no legal corridor or international convention; (4) Moral hazard; concerns about privacy, sensitive issues; (5) The subjective nature of programmers. (6) Cyber security, hacking risk; (7) Machine, AI violates who will take the responsibility?; (8) Technology gap for some countries; (9) Loss of control with AI: Who controls the world?
– AI controls the real and virtual integrated system model in Smart City
– AI provides mechanisms and policies to support businesses (the vitality of the economy) in Smart City.
– AI application in Smart government model, AI Government
– AI integrated in Smart Movement Model
– AI integrated in Smart Port Management Model
– AI manages and monitors intelligent environment (Land, water, air environment, seaports, coastal strip and river basins)
– AI Monitors resident
– AI controls non-traditional security threats
– AI supports the training of adaptive new human resources and the strategy of creating adaptive human resources, fostering and retraining to create human resources to meet the requirements.
– AI helps control the city to become safer, healthier and more efficient
– AI helps build a Smart City model to meet Security, Safety and Safety criteria.
– AI manages city planning and construction from the perspective of considering this as a complex digital ecosystem in terms of economy – society – technology, using Big data and IoT in its operations.
– AI and robot promote highly efficient production
(1) – Artificial intelligence: the foundation of the smart city and the model Artificial Intelligence World Society (AIWS); Building a widespread AI network: AI of Things (AIOT), every urban management field serving residents is based on an artificial intelligence platform that connects anytime, anywhere.
(2) – AIWS must be governed by artificial intelligence indicators of Security – Security – Safety, providing AI solutions and validating electronic markers by block chain.
(3) – AIWS must develop ISO standards on urban ethics and civilization. AIWS residential innovation is integrated, linked and shared to serve businesses and improve the quality of urban services.
(4) – AIWS associated with the Digital Government, the Government of Artificial Intelligence (AI Government). AIWS’s space is not limited by geographical space and can share and connect cultures to build harmonious societies.
(5) – AIWS must strengthen the sharing economy, improve electronic payments, use digital money, block chains to help GDP growth, monitor budget revenues, prevent money laundering, reduce crime.
(6) – AIWS must offer solutions to control virtual world crisis and limit negative impacts on the real world.
(7) – AIWS must strengthen the economy of customer care, marketing, sales and content production
(8) – AIWS must increase the transparency; all decisions, all activities of the City Government, functional agencies must be easy to check and supervise in order to ensure effectiveness.
(9) – AIWS must promote the development of self-management skills, such as proactive learning, resilience, stress tolerance and flexibility.
Step 1. Plan virtual space, real – virtual connection space
Step 2. Build the AIWS urban civilization and ethics indexes on the basis of connecting indicators ISO 37120: 2018 and ISO 37122: 2019 Smart City.
Step 3. Establish social Contract Agreement on Artificial Intelligence
Step 4. Develop a legal corridor to broadly recognize the legitimate AIWS model.
Step 5. Exploit block chain platform and connect existing artificial intelligence and provide access and exploitation to all levels of urban government – each household, citizen.
Step 6. Connect World Leaders, Mayors, Urban Professionals and Innovative Scientists to create data banks for AIWS and machine learning.
Step 7. Enhance the city’s competitiveness, resilience to natural disasters, catastrophes and economic crises.
Step 8. Test AI centers at all levels of urban government – connecting people. Revise and bring AIWS to the people of Smart City, towards a city of worth living, city of value.
7- STRATEGY FOR DESIGNING AND GOVERNING ARTIFICIAL INTELLECTUAL SOCIAL CITIES
8. Research on building a model of Smart City (Smart City) in association with the Artificial Intelligence World City (AIWS City) in several specific localities in VietnamI. Hai Phong city:1.1 Geo-political, geo-economic situation- Hai Phong is one of the five cities that are directly under the Central Government. On May 9th, 2003, the Prime Minister issued Decision No. 92/2003/QD-TTg on recognizing Hai Phong city as a first-class metropolis, a national level center.- Hai Phong is located downstream of the Thai Binh river system in the Red River Delta; bordering the provinces of Quang Ninh, Hai Duong, Thai Binh and bordering the East Sea with a coastline of 125km, where there are 5 large estuaries flowing into the sea. Hai Phong is 100 km from Hanoi, connected by road (expressway, national highway five) and railway. – The city has an area of 1,561.8 km2 consisting of 15 administrative units (7 urban districts, 6 rural districts and 2 island districts (Cat Ba Islands with 388 islands and Bach Long Vi island, located in the Gulf of Tonkin – 129,000 km2). The city has more than 2 million people, of whom more than 40% live in urban areas. Hai Phong is both an industrial city and a seaport city.- An industrial city, with its position, potential and strength as a driving force in the Northern key economic region; Located on two corridors – one belt of Vietnam – China economic cooperation; A seaport city, an important traffic hub of the country, with sea transport system, roads, highways, railways, international airports; it is the main gateway to the sea of Hanoi and northern provinces; – Having an important role and key position in economic, defence and security domains of the North and the whole country.SWOT analysisStrengthHai Phong has advantages in socio-economic development; identified as an important growth pole of the northern dynamic economic region; a key marine economic hub; one of the major industrial and commercial centres of the whole country and the centre of services, tourism, fisheries, education and health of the northern coastal region. Hai Phong has always maintained the second place regarding economic scale of the Red River Delta, the Northern key economic region, after Hanoi capital. It has played the role of a growth pole in the Ha Noi – Hai Phong – Quang Ninh economic triangle and has increasingly contributed to the national economy. Economic growth (GRDP) in 2019 reached 16.68%, 2.4 times higher than the national average.- It can be said that Hai Phong is a city with higher economic potential than many other localities in the country. It ranks the third in the country in terms of large number of enterprises with about 29,000 enterprises. – As the focal point of international integration of the Northern region, Hai Phong has the advantage of traffic infrastructure, acting as a driving force for the development of the whole region. The completion of the construction of Hai Phong international gateway port, Bach Dang bridge and the highways connecting to Ha Long, expanding national highway 10, coastal road from Quang Ninh
to Thanh Hoa, Hai Phong international gateway port, upgrading Cat Bi international airport, Tan Vu – Lach Huyen 2 bridge, Dinh Vu – Cat Hai economic zone, and others will create a strong development momentum for Hai Phong in the coming years, especially in the areas of investment attraction, export, marine transport, supporting industries, services and tourism. – Hai Phong has the advantage of sea, sea tourism, favourable for marine economic development, especially deep seaport, sea tourism. Its marine areas have large reserves of seafood to facilitate the development of fishing, aquaculture and seafood processing. – Regarding tourism, Do Son peninsula and Cat Ba Archipelago are very convenient for developing eco-tourism in the direction of forest – sea – island. The Cat Ba Archipelago has been recognized by UNESCO as a World Biosphere Reserve, a special national relic, as well as the National Park and Marine Protected Area of Vietnam. Cat Ba island has beautiful beaches in the landscape with majestic 388 small and large islands. Lan Ha Bay connects to the world natural heritage Ha Long Bay. Do Son Peninsula with many beaches, beautiful scenery, is a popular tourist attraction.- Hai Phong has attracted many major tourism development projects such as: an entertainment area and high-class eco-park in Vu Yen island (Vingroup); a cargo port, a tourist pier, a cable car station, tourist products production factory and tourism logistics service centre in Cat Ba (Sungroup). Hai Phong has approximately 500 hotels with 9,621 rooms as well as 70 travel businesses. – Hai Phong has advantages of human resources: Human resources are abundant, trained with higher quality than most of provinces and cities in the Red River Delta. The percentage of trained workers in the city is now over 75%, higher than the region and the country.- As a centre – the driving force for regional development, a leading important coordinate for international integration and competition of the country, the city has more advantages over other provinces in the competition for high-quality human resources attraction. It is forcasted that the city’s population will be about 2.4 – 2,7 million people, and about 4.3 – 4.6 million people by 2045.WeaknessesRegarding population, human resources:– The labour forces are insufficient in quantity and low in qualifications, lack of leading experts and excellent hi-tech experts. – Small population size (less than two million people, equal to 22% of Ho Chi Minh City, about 26% of Ha Noi), the attractiveness of human resources is not really high, population growth rate is low, especially population change. Mineral resources, tourism: – Mineral resources are limited, mainly are sand for landfill, limestone, and mountain land with reducing reserves.- The quality of tourism services in several tourist areas is still low, not meeting the requirements of tourists.Traffic infrastructure: – Urban and port traffic jams due to the large number of container trucks entering and leaving ports through the city.- While the infrastructure system, despite being upgraded and strongly developed, still lacks synchronization, does not meet the requirements of industrialization and modernization. Specifically, the water and rail transport system is underdeveloped.- Internal transport infrastructure is slowly expanded and upgraded; there has been inner city traffic jams; traffic connecting to the port has seriously degraded and congested frequently; traffic connection with other localities in the the region is still limited.- Logistics infrastructure has not developed to match the potential and strength of the port city.Regarding economic domain: The economic structure of Hai Phong is service – industry (accounts for 89.3 % in 2019), land for non-agricultural production and business accounts for only 5%, agricultural land still accounts for over 50%.
– Hai Phong has not fully utilized the potential and advantages of the city as well as the role of the growth pole, the impact of spill-over and linkages in the region, even its in GDP contribution has decreased in the Red River Delta region. The quality of economic growth has not really ensured sustainability, the total factor productivity (TFP) has not contributed much to growth, low labour productivity. Limited application of high technology in production, not acting as the centre of science and technology of the region. Enterprises in the area are not strong. Supporting industry has not yet developed. Economic restructuring remains slow.
– Hai Phong’s provincial competitiveness index has improved but many indexes are still low. Hai Phong still ranks behind other provinces and cities in the region and other cities under the central government. (In 2019: ranked 10th of 63 provinces and cities). Administrative reform shows signs of going down. Effectiveness and efficiency of state management are not high. The orientation to improve international competitiveness is not strong.
– City’s business force is not strong, lack of development pillars which are strong private economic groups.
– Pollution risk due to industrial and urban development. Rế river, Đa Độ river and Giá river which supply domestic water have high risk of pollution.
Opportunities
– Hai Phong is a port city with a rich history, strong traditions and aspirations for innovation, and a higher level of development than most other provinces and cities in the Red River Delta.
– The economic growth rate, the urbanization rate of the city in recent years is higher than most provinces in the region and the country.
– Socio-economic infrastructure is more and more complete and modern, especially transport and urban infrastructure, creating a strong driving force for Hai Phong in the next coming years, especially in fields attracting investment, logistics, trade, shipping, etc.
– Many large projects and key projects that have a role in the Red River Delta in the North have been prioritized by the Central Government to invest in building new projects and upgrading existing ones (expressways, an international airport, international gateway ports, over-the-sea bridges, and other things).
– Being in the centre of the Northern coastal area, an important traffic hub, the main gate to the sea of Northern provinces, Hai Phong has more favourable conditions than other places in economic development, integrating into the international economy, receiving the scientific and technological achievements of the world.
– Hai Phong is considered as one of the 10 most attractive investment locations. The Fourth Industrial Revolution has impacted on all nations around the world, provided many opportunities and advantages for nations in general and cities in particular for building the smart city. Hai Phong can learn experiences from other countries; learning core technologies such as AI, IoT, IT and other things.
– At the same time, the world is in the right moment, converging many conditions to carry out the building of smart city, as more and sciences and technologies have grown rapidly, robots and artificial intellectual devices have been produced commercially in many fields.
– In 2014, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen Van Thanh – Former Municipal Party Committee Secretary, Former Chief of Hai Phong People’s Committee, member of the International Society for Systems Sciences (ISSS) directed to implement system thinking training in state management for 40,000 participants (including officers, civil servants, public servant, teachers at all levels, students).
– In addition, the World Council on City Data (WCCD) has collaborated with ISO Switzerland to issue ISO 37120 – Sustainable Community – Indicators on Urban Services and Quality of Life and ISO 37122:2009 on smart city. This is considered as the premise for the study of metropolitan indicators and management of smart city according to international standards.
Challenges
– Climate change and rising sea levels due will pose increasingly serious challenges for the development of coastal cities such as Hai Phong. It is forcasted that Hai Phong is one of 10 cities in the world suffering the most because of severe sea-level rise.
– There remains many shortcomings in urban development and management. There are many hollow urban areas, with slow development of infrastructure and housing.
– Environmental pollution, especially water and air environment, directly affecting the livelihood of people, has been complicated. Technical infrastructure for environmental protection has not met the speed of urbanization. The status of waste discharge causing environmental pollution has not been detected and handled in time.
– Pollution of soil, water, especially port waters; air pollution, especially in industrial parks, solid waste at Dinh Vu and Trang Cat garbage landfills, rural landfills, and other things.
– The thread of traffic jams to Cat Ba island and air pollution when the traffic flow to the island is overloaded and tourism is developing.
– In the process of building a smart city, cities also face many common challenges because of the world situation, such as the impacts of non-traditional security (28 global risks); the risks from emerging technologies and other things.
– At the same time, Vietnam also has limitations in accepting the impacts of the 4.0 industrial revolution such as lack of synchronization, developmental bias, mere appearance of e-commerce (of the 15 main areas of the fourth industrial revolution). There is no technology appearing in the list of 10 emerging technologies announced in 2017 related to smart cities. Therefore, this is also considered a challenge for Hai Phong in particular.
– The negative impact of the forth industrial revolution poses a risk of technological lag, productivity decline; Overexploitation of skilled and low-skilled labour has disrupted the traditional labour market; loss of security, information security, copyright infringement, lack of qualified human resources.
– The labour market is developing in the direction of increasing quality requirements, qualifications and quantitative restrictions. This poses a challenge to vocational training for rural workers.
Determining the smart adaptive model of Hai Phong city
– Appling systems thinking in smart city building (find leverage points to influence, control city as an ecosystem).
– Building smart city model “characteristics of a port city, traffic hub”.
– Attach great importance to nature when planning for smart cities in relation with conservation and sustainable development.
– Smart island and marine space management and smart coastal ecosystem management.
– Transforming the economy of the city to a green economy based on the application of advanced science and technology in key areas.
– Building Hai Phong into a liveable city, attractive and dynamic with the criteria: attracting more and more businesses and investors opening representative office in Hai Phong; attract talents/intellectuals, skilled workers to work, live; is a destination in tourism, sports, culture and enjoy the high living conditions.
– Building important infrastructures for development of industry, services, tourism and trade. Building a national and international logistics service centre in Lach Huyen. To complete the modern infrastructure and bring into full function of the Dinh Vu – Cat Hai economic zone. To build Hai Phong into a national and regional centre for shopping and entertainment services.
– Establishing competitive enterprises, standing in the top of the big corporations in the whole country, towards the whole region.
– Hai Phong is a major marine economic centre of the country with diversified and dynamic development with a focus on marine human resources training, marine science and technology, marine medicine; shipping devices and equipment manufacturing; Island tourism centre of international level.
– Becoming a national innovation centre; Centre for human resource development and training.
– Investing in building a new urban area north of Cam river and become a smart urban centre.
– Initially developing smart elements in the field of transport, tourism, health, environment, energy, security and order…
– Achieving the basic criteria of smart city, located in the group of the liveable cities in Southeast Asia. Complete the construction of public transport system with smart and environmentally friendly.
– Becoming a modern national logistics centre with high competitiveness and cooperation. To formulate smart urban projects combining tourism services with world-class resorts; green parks combined tourism.
– Comprehensive and modern infrastructure system in all types of traffic; direct connections to continents by sea and air; convenient connections to the northern provinces and southwestern China, northern Laos by expressway, high speed rail and airways. To study and deploy the investment in the construction of the airport in Tien Lang.
– Completing important infrastructure works of regional-linking nature; synchronous, modern, intelligent urban infrastructure.
– Using planning as a tool to orient, manage smart urban in accordance with principles and motto: (i) “Development for conservation – conservation for development”; (ii) “Planning, design must follow the rules of nature”; (iii) “Planning first – then construction”; (iv) “Planning first – then investing”; (v) “Project first – then implementation”; (vi) “Under the ground first – then on the ground”; (vii) “Management according to eco-city design indicators”; (viii) “The goal is to reach the value, lifeful, competitive, resilient city”. “No development first-then repairing”.
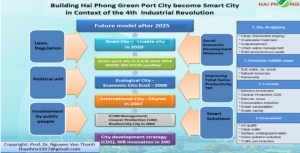
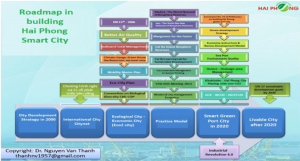

Geo-political, geo-economic situation
– Bac Ninh is the ancient centre of Kinh Bac, holy land with extraordinary people, the largest principal graduate in the country. In the national examinations under feudal dynasties, there was 17 principal graduates and 622 doctors. This is also the land has many cultural heritage, many festivals, traditional craft villages. The province was re-established on January 1st, 1997.
In 2017, Bac Ninh city was recognized as a first-class city under Bac Ninh province. The province is also striving to build Bac Ninh into a under government city by 2022.
Bac Ninh has the smallest area (822.7 km2), but the third highest population density in the country.
Bac Ninh is only 30km from the capital of Hanoi, in the construction planning of the Capital Region; It is convenient for transportation to connect with Hanoi capital and Northern provinces.
In addition, Bac Ninh is located on two economic corridors: (i) Kunming – Lao Cai – Hanoi – Hai Phong – Quang Ninh and (ii) Nam Ninh – Lang Son – Ha Noi – Hai Phong – Quang Ninh.
The terrain of the province is not entirely plain but alternating with low hills. Bac Ninh has a relatively dense network of rivers, the density of river nets is quite high, the average is from 1 to 1.2 km / km2; There are 3 large river systems flowing from Duong River, Cau River, Thai Binh River.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
– Bac Ninh has advantageous location, in the Capital Region.
– Bac Ninh’s economy is in a “miraculous” development period, maintaining a GDP growth rate of 15% annually during the past 20 years. The average labour productivity of the province in the period 2010-2018 is estimated to increase 3.6 times, from 197 million VND to 274 million VND. Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) of the province in 2017 accounts for 3.11% of GDP in the whole country, ranking fourth in 63 provinces. Industrial production growth was high, export turnover reached a record of 14.9% of total export turnover nationwide and held the second position in 63 provinces and cities, making Bac Ninh become the centre of production, high-tech electronics industry of the region and the world.
– The province is in the period of golden population structure.
– Dynamic provincial leaders, having a strong desire to develop, clear mechanism, good administrative reform, provincial competitiveness index PCI is always at the top of the country.
– Bac Ninh has a long history of tradition and cultural convergence in the Red River Delta. This is also a land of traditional hospitality; The people are hospitable, diligent and creative, with skillful hands bearing boldly folk characteristics of a hundred areas such as silk, ceramics, bronze casting, silver engraving, wood engraving, paper making, folk paintings, outstanding folk songs
Weaknesses
– Bac Ninh has the smallest area (822.7 km2).
– The province is at risk of environmental pollution due to industrial development, urban and craft villages. Environmental pollution of craft villages in Bac Ninh is at a particularly serious level. In addition, the pollution of some factories in industrial parks also affects to the lives and health of people and workers.
– Besides, Bac Ninh is poor in mineral resources, mainly building materials such as clay for brick, tile, pottery…
Opportunities
– The 4.0 industrial revolution has impacted many countries around the world, bringing many opportunities and advantages to nations in general and cities for building smart cities. Bac Ninh province can learn from experience in other countries; learning core technologies such as AI, IoT, IT…
– At the same time, the world is in the right place, converging many conditions to build smart city, as more and more science and technology has grown rapidly, robots and AI devices have been Commercial production serves many fields…
– In addition, the World Council on City Data (WCCD) has coordinated with ISO Switzerland to issue ISO 37120 – Sustainable Community – Urban Services and Quality of Life Index. This is considered as the premise for the study of city metrics and city management according to international standards.
– Being the smallest country in the country, Bac Ninh is one of the few provinces and cities to attract the largest foreign direct investment and the convergence of leading multinational corporations and high-tech enterprises such as Samsung, Canon, Foxconn, Microsoft, Hanaka…
Threats
– In the process of building a smart city, cities also face many common challenges brought about by the world context, such as the effects of traditional security (global risks); the risks from emerging technology…
– At the same time, Vietnam also has limitations in accepting the impact of the 4.0 industrial revolution, inconsistent, developmental bias (focusing on e-commerce among the 15 main areas of the industrial revolution 4.0), There is no technology appearing in the list of 10 emerging technologies announced in 2017 related to smart cities … Therefore, this is also considered a challenge for Vietnam in general, Bac Ninh province in particular.
– Besides, there are also many subjective challenges from cities. For Bac Ninh province, when building a smart city, this will be a leading city in testing new science and technology areas in the delta and midland areas; The province also faces many challenges such as financing; To control the environmental pollution of land, water and air while still maintaining industrial production growth.
Determining the smart and adaptive model of Bac Ninh province
– Connect the metropolitan area to the North pole provinces.
– Apply systems thinking in building Smart City (find leverage points to influence, control city as an ecosystem).
– Find the characteristics and identity of the ancient Kinh Bac region with the traditional (refer to the method of Paris, France to build smart cities associated with the preservation of ancient architecture and cultural identity).
– Conservation of village space in Bac Ninh city and 1,500 historical-cultural relics, of which more than 500 relics are ranked.
– Focus on natural factors when planning conservation are three rivers (Cau river, Duong river, Ngu Huyen Khe river) and the remnants of the natural ecosystem and landscape; The culture and geography “river, mountain” features.
– Smart City Model Represents Timeline: “Past – Present – Future”. Inheriting past achievements, integrating and preserving the principle of conservation to develop, developing for conservation.
– Use planning as a tool to orient, manage smart cites in accordance with principles and motto: (i) “Development for conservation – conservation for development”, (ii) “Planning, design must follow the rules of nature”, (iii) “Planning first- then construction”, (iv) “Planning first – then investing”, (v) “Project first – then implementation”, (vi) “Under the ground first – then on the ground”, (v) “Management according to eco-city design indicators”, (vi) “The goal is to reach the value, lifeful, competitive, resilient city”, (vii) “No development first – then repairing”.
– The area of Can Tho was discovered and appeared on Vietnamese maps since 1739, named Tran Giang. Can Tho is the West Capital-the central of the South West of Viet Nam from hundred years ago, located in the heart of the Mekong Delta.
– Can Tho is the first-grade city, a city under the Central Government and one of four provinces and cities in the key economic region of the Cuu Long river Delta and the fourth key economic region of Vietnam.
– It is an important transportation hub for waterways, roads, sea routes, air routes, and regional, national and international routes; shared border with Dong Thap and Vinh Long provinces in the east, Kien Giang province in the west, Hau Giang province in the south and An Giang province in the north. This city is the place that connects the Mekong delta with domestic and Cambodian; connecting the coastal, ocean and ocean ranges to Southeast Asia.
– Can Tho is a lowland urban area with the Mekong River alluvial origin, which connects ecological zones of river systems and ditches to ensure the objectives of development and conservation – conservation and development.
– This area has fresh and brackish water ecosystems, suitable for planting trees: water coconut, rice …; and freshwater aquaculture.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
– Can Tho is a new land, rich in natural resources with great biological capacity, high biodiversity.
– Can Tho located in the Mekong Delta – the barn of the country (food security).
– This place has a long history, cultural convergence area, good people.
Weaknesses
– Can Tho is affected by climate change and sea level rise. Viet Nam is one of the five countries affected by climate change, the Mekong River Delta is a heavily impacted region.
– It is a region with high biodiversity but in which mangrove ecosystems are at risk of destruction.
– Can Tho is the low area at the bottom of the water source, water sources and sediment from upstream are threatened, with a high risk of serious injury.
Opportunities
– The 4.0 industrial revolution has impacted many countries around the world, bringing many opportunities and advantages to nations in general and cities in particular for the purpose of building smart cities. Can Tho City can learn from experience in other countries; learning core technologies such as AI, IoT, IT…
– At the same time, the world is in the right moment, converging many conditions to build up smart city, as more and more science and technology has grown rapidly, robots and AI devices have been commercially produced serving many fields …
– In addition, the World Council on City Data (WCCD) has coordinated with ISO Switzerland to issue ISO 37120 – Sustainable Community – Urban Services and Quality of Life Index. This is considered as the premise for the study of city metrics and city management according to international standards.
Threats
– In the process of building a smart city, cities also face many common challenges brought about by the world context, such as the effects of traditional security (28 global risks); the risks from emerging technology.
– At the same time, Vietnam also has limitations in accepting the impact of the 4.0 industrial revolution, the lack of synchronism, development bias, only appeared in the field of e-commerce (in 15 main areas of the industry 4.0), Thereis no technology appearing in the list of 10 emerging technologies announced in 2017 related to smart cities … Therefore, this is also considered a challenge for Vietnam in general, Can Tho in particular.
– Besides, there are also many subjective challenges from cities in particular. For the city of Can Tho, when building a smart city, this will be a leading city in testing new science and technology in the river basin, lowland; Can Tho also face many challenges in effective management of resources, protection of biodiversity of salty forest.
3.2. Determining the smart and adaptive model of Can Tho city
Connecting regions
– Apply systems thinking (find leverage to influence, control city as an ecosystem).
– Find the characteristics and identity of West Capital with outstanding features such as biodiversity, connectivity, mangrove ecosystems.
– Using planning as a tool to orient, manage smart urban in accordance with principles and motto: (i) “Planning first- then construction”, (ii) “Planning first–then investing”, (iii) “Project first – then implementation”, (iv) “Under the ground first –then on the ground”, (v) “Management according to eco-city design indicators”, (vi) “The goal is to reach the value, lifeful, competitive, resilient city”.
Industrial revolution 4.0 will significantly change the world in 2025 (according to a survey of Technology Pioneers in 2020 and the assertion of Associate Professor, Dr Nguyen Van Thanh):
(1). Manufacturing on the basis of artificial intelligence optimization (AI-optimized manufacturing)
(2). A new era of computing with quantum computing
(3). A far-reaching energy transformation to significantly reduce carbon emissions
(4). 5G will enhance the global economy and save lives
(5). Healthcare paradigm shift to prevention through diet
(6). A new normal in managing cancer
(7). AI and Robotic retail
(8). A blurring of physical and virtual spaces, block chain crypto-currency crowned
(9). Putting individuals – not institutions – at the heart of healthcare
(10). The future of construction has already begun
(11). Gigaton-scale CO2 removal will help to reverse climate change
(12). A new era in medicine
(13). Closing the wealth gap and remote area gap
(14). A clean energy revolution supported by digital twins
(15). Understanding the microscopic secrets hidden on surfaces.
(16). Machine learning and AI expedite decarbonization in carbon-heavy industries
(17). Privacy is pervasive – and prioritized
(18). Smart cities are increasingly popular thanks to ISO technology and standardization.
(19). Major changes in city governance model adapting to the inception and development of smart cities, smart countries: Artificial Intelligence Government (AI-Government) and Social Intelligence World City (AIWS City). Transformation model from current cities to smart cities
(Source: Building and Management of Smart Cities, Associate Professor Dr. Nguyen Van Thanh – The Truth National Political Publishing House, 2020)
Nguyen Van Thanh – The Truth National Political Publishing House, 2020)
Application of systems thinking science to guide systems, impact the lever point for building the circular economy ecological model that applies systems thinking in the fourth industrial revolution (authored by Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Van Thanh):
Step 1: Constructing the systems thinking model, identifying the lever point.
Step 2: Developing the main criteria for evaluation (in accordance with the following principle: Planning goes first; Taking nature as a model; Taking nature as a measure; Taking nature as a driving force, nature is the source of inspiration; Agreement with nature)
Step 3: Analyzing the flows of raw materials and fuel according to rotating principle, optimizing inventory levels, zero waste.
Step 4: Maintaining balance between production and waste, applying the technologies of the fourth industrial revolution.
Step 5: Changing to use recyclable energies and new materials.
Step 6: Building ecological industrial zones with zero waste cycle and self-balance of recyclable energy source.
Step 7: Identifying industrial symbiosis relationships (waste of a factory becomes inputs of another factory).
Step 8: Orienting, guiding consumption according to the 6R model (Reduce – Reused – Recycle – Refuse – Rethink – Responsibility), viewing products as services (changing ownership thinking to usage thinking).
Step 9: Promoting share economy, common use, maximum exploitation of redundant use and capacity of products and services in the economy.
In recent years, with the outbreak of applying information and communication technology (ICT) in many fields, “smart city” has become the standard model of many modern cities in the world. However, the development of “smart city” does not only base on advanced technology but also requires a “smart management” system, ensuring integrated and compatible network between new technological elements and local characteristics. Building a model of “smart city governance” that incorporates the content of an artificial intelligence world city (AIWS City) is something that many local governments in Vietnam need to study from previous experiences of developed cities in the world. The research and development of AIWS and the gradual inclusion of Vietnamese cities in this model to effectively manage Smart City is an important step for the future.
The future will be formed on the basis of real-virtual, all-thing, global, system-system, people-robot and AI connections.
AI World Society - Powered by BGF