AIWS Peace Symphony Takes Center Stage as Global Leaders Unite for Music and Humanity
July 4, 2025
This week in the History of AI at AIWS.net – the creation and expansion of ARPANET. ARPANET stands for the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, and was a project that was funded by ARPA and the DoD.
While urban myths claim that ARPANET was developed for communications that would survive a nuclear attack, it was actually intended to build packet switching, rather than circuit switching, which had been the traditional method of communications. Charles Herzfeld, the director of ARPA between 1965–1967, also stated that the goal was to connect the various research computers in the country, which were separated by the plain fact of geography.
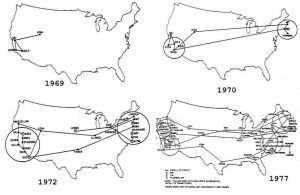
ARPANET was developed in the late 60s, with four universities being the first hosts – Stanford (through the SRI lab), UCLA, UCSB, University of Utah School of Computing. In 1970, the network expanded to the East Coast, including MIT and Harvard. By 1973, the UK and Norway were added to the network through University College London and the Norwegian Seismic Array (NORSAR) respectively. It was decommissioned in 1990.
Eventually, ARPANET would lay the foundations for the Internet, which is commercialized rather than specialized. It is for this reason that the History of AI considers it a milestone in the development of AI and the Internet of Things.
AI World Society - Powered by BGF